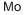Molybdenum standard , 100ug/mlin1%HCl , 7439-98-7
CAS NO.:7439-98-7
Empirical Formula: Mo
Molecular Weight: 95.94
MDL number: MFCD00003465
EINECS: 231-107-2
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 20ml | RMB79.20 | In Stock |
|
| 50ml | RMB127.20 | In Stock |
|
| 80ML | RMB191.20 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 2617 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 4612 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 10.3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| bulk density | 1400kg/m3 |
| refractive index | 2.81 (740 nm) |
| Flash point: | -23 °C |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | wire |
| color | Gray |
| Specific Gravity | 10.2 |
| PH | 9.2 (20°C in H2O) |
| Flame Color | Yellowish green |
| Resistivity | 5.0 μΩ-cm, 20°C |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble inwater. Soluble innitric acid andsulfuric acid. Slightly soluble inhydrochloric acid. |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 13,6257 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 3 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 5000 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Powder is flammable. |
| Bulk Modulus | 272 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 330 GPa 160 GPa (@Temperature 2000 °C ) 200 GPa (@Temperature 1800 °C ) 250 GPa (@Temperature 1400 °C ) 275 GPa (@Temperature 1000 °C ) |
| Shear Modulus | 120 GPa |
| Hardness, Vickers | 200 |
| Poissons Ratio | 0.38, calculated |
| Hardness, Brinell | 225, Converted from Vickers for 3000 kg load/10 mm ball Brinell test. Annealed |
| Hardness, Rockwell A | 60, Converted from Vickers. Annealed |
| Hardness, Rockwell B | 98, Converted from Vickers. Annealed |
| Hardness, Rockwell C | 19, Converted from Vickers. Annealed |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7439-98-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Molybdenum (7439-98-7) |
Description and Uses
Molybdenum is an essential trace mineral associated with several enzyme systems required for the normal body functions. Mine workers have developed symptoms of molybdenosis. The significantly expanding or softening property of the material makes it useful in applications that involve intense heat, including the manufacture of aircraft parts, electrical contacts, industrial motors, and filaments.
The high melting point of molybdenum is the major determinant of how it is used. Its chiefuse is as an alloy in the manufacture of engines of automobiles. “Moly-steel” contains up to8% molybdenum and can withstand high pressures and the relatively rapid changes of enginetemperatures (e.g. cold engine to hot and back again without the metal warping and with theability to withstand excessive expansion and contraction).
Its high melting point also makes it useful for metal electrodes in glassmaking furnaces.Molybdenum’s high resistance to electricity makes it useful in high-temperature filament wiresand in the construction of parts for missiles, spacecrafts, and nuclear power generators.
Molybdenum is also used as a catalyst in petroleum refining, as a pigment for paints andprinter’s ink, and as a high-temperature lubricant (molybdenum disulphide-MoS2) for use byspacecraft and high-performance automobiles.
In hospitals, radioisotope Mo-99, which decays into technetium-99, is given internally tocancer patients as a “radioactive cocktail.” Radioactive Tc-99 is absorbed by tissues of cancerpatients, and then x-ray-like radiation is used to produce pictures of the body’s internal organs.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS08 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H228-H361f |
| Precautionary statements | P202-P210-P240-P241-P280-P308+P313 |
| Hazard Codes | F,Xi,N,Xn |
| Risk Statements | 36/38-11-67-65-62-51/53-48/20-38 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-16-9-62-61-36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN 3264 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | QA4680000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HazardClass | 4.1 |
| PackingGroup | III |
| HS Code | 81029600 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 7439-98-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| IDLA | 5,000 mg Mo/m3 |
| Limited Quantities | 1.0 Kg (2.2 lbs) |
| Excepted Quantities | Max Inner Pack (30g or 30ml) and Max Outer Pack (500g or 500ml) |