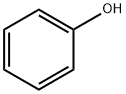
Phenol , ACS , 108-95-2
Synonym(s):
Phenol;Phenol solution;Hydroxybenzene;C?H?O;Tris-equilabrated Phenol
CAS NO.:108-95-2
Empirical Formula: C6H6O
Molecular Weight: 94.11
MDL number: MFCD00002143
EINECS: 203-632-7
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 40-42 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 182 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.071 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| bulk density | 620kg/m3 |
| vapor density | 3.24 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.09 psi ( 55 °C) |
| FEMA | 3223 | PHENOL |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 175 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | liquid |
| pka | 9.89(at 20℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.071 |
| color | faintly yellow |
| PH | 6.47(1 mM solution);5.99(10 mM solution);5.49(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | Sweet, medicinal odor detectable at 0.06 ppm |
| Odor Threshold | 0.0056ppm |
| explosive limit | 1.3-9.5%(V) |
| biological source | synthetic |
| Odor Type | phenolic |
| Water Solubility | 8 g/100 mL |
| FreezingPoint | 41℃ |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7241 |
| JECFA Number | 690 |
| BRN | 969616 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.09 at 5 °C (average derived from six field experiments, Lüttke and Levsen, 1997) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA skin 5 ppm (~19 mg/m3 )
(ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); 10-hour TWA 5.2 ppm (~20 mg/m3 ) (NIOSH); ceiling
60 mg (15 minutes) (NIOSH); IDLH 250
ppm (NIOSH). |
| Dielectric constant | 4.3(10℃) |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | PRESERVATIVE ORAL CARE FRAGRANCE DENATURANT ANTIMICROBIAL DEODORANT |
| InChIKey | ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 1.47 at 30℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 108-95-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 47, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol(108-95-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenol (108-95-2) |
| Absorption | cut-off at 294nm in H2O at 0.5M |
Description and Uses
Phenol is a stable chemical substance and appear as colourless/white crystals with a characteristic, distinct aromatic/acrid odour. It is reactive and incompatible with strong oxidising agents, strong bases, strong acids, alkalis, and calcium hypochlorite. Phenol is flammable and may discolour in light. Phenol is used in the manufacture or production of explosives, fertiliser, coke, illuminating gas, lampblack, paints, paint removers, rubber, perfumes, asbestos goods, wood preservatives, synthetic resins, textiles, drugs, and pharmaceutical preparations. It is also extensively used as a disinfectant in the petroleum, leather, paper, soap, toy, tanning, dye, and agricultural industries.
The predominant use of phenol today is for phenolic resins.it is a powerful bactericide,phenol can be found in numerous consumer products includingmouthwashes,antiseptic ointments,throat lozenges,air fresheners,eardrops,and lipbalms.
Phenol continues to be a primary chemical used to make thermoset resins.These resinsare made by combining phenol with aldehydes such as formaldehyde.More than 4 billionpounds of phenolic resins are used annually in the United States.Phenolic resins findtheir widest use in the construction industry.They are used as binding agents and fillers inwood products such as plywood,particleboard,furniture, and paneling.Phenolic resins areimpregnated into paper,which,after hardening,produces sheets that can be glued togetherto form laminates for use in wall paneling and countertops.Decking in boats and docksare made from phenolic resin composites.Phenolic resins are used as sealing agents andfor insulation. Because phenolic resins have high heat resistance and are good insulators,they are used in cookware handles.Because they are also good electrical insulators,they areused in electrical switches,wall plates, and for various other electrical applications.In theautomotive industry,phenolic resins are used for parts such as drive pulleys,water pumphousings, brakes,and body parts.
In addition to the construction industry,phenol has many other applications.It isused in pharmaceuticals,in herbicides and pesticides,and as a germicide in paints.It can beused to produce caprolactam,which is the monomer used in the production of nylon 6.Another important industrial compound produced from phenol is bisphenol A,which ismade from phenol and acetone.Bisphenol A is used in the manufacture of polycarbonateresins.Polycarbonate resins are manufactured into structural parts used in the manufactureof various products such as automobile parts,electrical products,and consumer appliances.Items such as compact discs, reading glasses,sunglasses,and water bottles are made frompolycarbonates.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS05,GHS06,GHS08,GHS09 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301+H311+H331-H314-H341-H373-H411 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P273-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338 |
| Hazard Codes | T,C,F,Xn |
| Risk Statements | 23/24/25-34-48/20/21/22-68-40-39/23/24/25-11-36-20/21/22-24/25 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-45-36/37-28A-28-24/25-1/2-36-16-7 |
| RIDADR | UN 2821 6.1/PG 2 |
| OEB | A |
| OEL | TWA: 5 ppm (19 mg/m3), Ceiling: 15.6 ppm (60 mg/m3) [15-minute] [skin] |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | SJ3325000 |
| F | 8-23 |
| Autoignition Temperature | 715 °C |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HazardClass | 6.1 |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29071100 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 108-95-2(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 530 mg/kg (Deichmann, Witherup) |
| IDLA | 250 ppm |
| Limited Quantities | 100ml (liquid) or 0.5 Kg (solid) |
| Excepted Quantities | Max Inner Pack (1g or 1ml) and Max Outer Pack (500g or 500ml) |