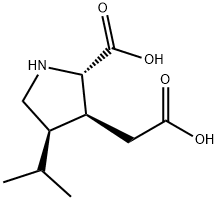
≥98%(HPLC),powder , 52497-36-6
Synonym(s):
2-Carboxy-4-isopropyl-3-pyrrolidineacetic acid
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 10mg | RMB2430.66 | In Stock |
|
| 50mg | RMB10821.21 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 285 °C (decomp) |
| Boiling point: | 416.6±30.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.187±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: >10 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 2.11±0.60(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in water |
Description and Uses
Dihydrokainic acid (DHK) is an inhibitor of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2; Ki = 23 μM for glutamate uptake by COS cells expressing EAAT2). It is selective for EEAT2 over EAAT1 and EAAT3 (Ki = >3 mM for both). DHK microinfusion (5 nmol) into the rat infralimbic cortex reduces the time spent immobile in the forced swim test, indicating antidepressant-like behavior, an effect that is blocked by the AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX and the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtype 5-HT1A antagonist WAY-100635 . It also increases glutamate and serotonin levels and the expression of c-Fos in the dorsal raphe nucleus. In contrast, DHK microinjection (6.25 nmol) into the rat prefrontal cortex (PFC) increases the latency to drink sucrose in a sucrose intake test, indicating anhedonia-like behavior. It also impairs memory acquisition, consolidation, and retrieval in mice in the novel object recognition test.
Dihydrokainic acid has been used as a glutamate transporter (GLT-1) inhibitor in the glutamate uptake assay of astrocytes and glial cells. It may be used as a GLT-1 inhibitor in Lateral habenula (LHb).
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H312-H332-H302 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P271-P304+P340-P312-P280-P302+P352-P312-P322-P363-P501-P264-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Statements | 20/21/22 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |