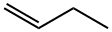1-Butene (ca. 10% in Hexane) , 106-98-9
CAS NO.:106-98-9
Empirical Formula: C4H8
Molecular Weight: 56.11
MDL number: MFCD00009383
EINECS: 203-449-2
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | −185 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | −6.3 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.5951 |
| vapor density | 1.93 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1939 mm Hg ( 21.1 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.3962 |
| Flash point: | 80 |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Soluble in alcohol, benzene, and ether (Weast, 1986) |
| pka | >14 (Schwarzenbach et al., 1993) |
| form | gas |
| color | Colorless to Almost colorless |
| Odor | Slightly aromatic |
| Odor Threshold | 0.36ppm |
| explosive limit | 9.3% |
| Water Solubility | 222 mg/kg at 25 °C (shake flask-GC, McAuliffe, 1966) |
| FreezingPoint | -185.35℃ |
| Merck | 14,1519 |
| BRN | 1098262 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (atm?m3/mol):
0.25 at 25 °C (Hine and Mookerjee, 1975) |
| Stability: | Volatile |
| InChIKey | VXNZUUAINFGPBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 2.35 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 106-98-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1-Butene (106-98-9) |
Description and Uses
1-Butene is a colourless, stable but polymerises exothermically, extremely flammable liquefied gas with an aromatic odour. It is insoluble in water and is one of the isomers of butane. 1-Butene readily forms explosive mixtures with air. It is incompatible with strong oxidising agents, halogens, halogen acids, metal salts, boron trifluoride, fluorine, and nitrogen oxides. 1-Butene of high purity is made by cracking naphtha and separating it from other products by an extra-high-purity distillation column. It is an important organic compound in the production of several industrial materials – for instance, linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), a more flexible and resilient polyethylene, and a range of polypropylene resins – and in the production of polybutene, butylene oxide, and the C4 solvents secondary butyl alcohol (SBA) and MEK. The vapour of 1-butene is heavier than air and may travel long distances to an ignition source and flash back.
Butenes are used extensively in gasoline production to produce high-octane gasoline compounds.Another large use of normal butenes in the petrochemical industry is in the production of 1,3-butadiene. Butene is used in the plastics industry to make both homopolymers and copolymers. Another use of 1-butene is in the production of solvents containing four carbons such as secondary butyl alcohol and methyl ethyl ketone (MEK).
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS04 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H220-H280 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P410+P403 |
| Hazard Codes | F+,F |
| Risk Statements | 12 |
| Safety Statements | 9-16-33 |
| RIDADR | UN 1012 2.1 |
| WGK Germany | - |
| F | 4.5-31 |
| Autoignition Temperature | 723 °F |
| Hazard Note | Extremely Flammable |
| DOT Classification | 2.1 (Flammable gas) |
| HazardClass | 2.1 |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 2901230000 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 106-98-9(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Excepted Quantities | Not Permitted as Excepted Quantity |