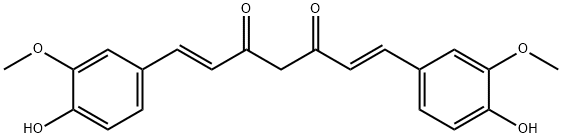
Curcuminsolution , 0.1%in?95%Ethanol , 458-37-7
Synonym(s):
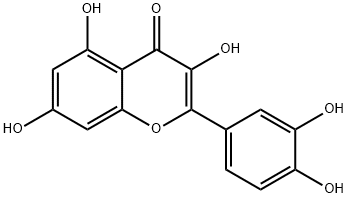
Curcumin;Diferuloylmethane;Diferulylmethane;Natural Yellow 3;(E,E)-1,7-bis(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione
CAS NO.:458-37-7
Empirical Formula: C21H20O6
Molecular Weight: 368.38
MDL number: MFCD01868798
EINECS: 207-280-5
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 100ml | RMB103.20 | In Stock |
|
| 500ml | RMB359.20 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 183 °C |
| Boiling point: | 418.73°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 0.93 |
| vapor density | 13 (vs air) |
| refractive index | 1.4155-1.4175 |
| Flash point: | 208.9±23.6 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 10 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 8.09(at 25℃) |
| Colour Index | 75300 |
| color | orange |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | Yellow (7.8) to red-brown (9.2) |
| biological source | Curcuma longa (Turmeric) |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble (hot) |
| λmax | 430nm |
| Merck | 14,2673 |
| Solvent | Ethanol |
| Concentration | 1 mCi/ml |
| Specific Activity | 5-15 Ci/mmol |
| BRN | 2306965 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be light sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Major Application | Cosmetics, drug-eluting stents, inhibition of formation of skin-wrinkles, treating alzheimer’s disease, skin diseases, coronary restenosis, diabetes, obesity, leukemia, neurofibromas, cancer, antimicrobial, antiviral, antiinflammatory, antiprostate cancer |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | ANTIOXIDANT COLORANT |
| InChIKey | VFLDPWHFBUODDF-FCXRPNKRSA-N |
| LogP | 3.290 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 458-37-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Curcumin (458-37-7) |
Description and Uses
The main source of curcumin is the root of Zingiberaceae Curcuma aromatica, rhizome of Curcuma longa (Jiang Huang), Curcuma zedoaria, and Acorus calamus. Among them, Jiang Huang contains about 3–6% curcumin. The traditional Chinese medicine, Jiang Huang, is the root tuber of perennial herbaceous plant Curcuma longa L. of family Zingiberaceae. It was firstly recorded in the “Tang materia medica” (Xin Xiu Ben Cao). It is pungent, bitter, and warm and enters the liver and spleen meridians. It activates the blood, moves qi, dredges meridians, and alleviates pain. In India and other Asian countries, Jiang Huang has more than 6000?years of application history. In Japan, Jiang Huang has a long history of health care, and the people of Okinawa Island regarded Jiang Huang as a holy tribute to the emperor. Jiang Huang mainly comes from Taiwan, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan, and Tibet of China and other regions in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It grows in warm and humid climate and sunny environment with abundant rainfall and fears cold frost, drought, and flood. At present, Chinese Pharmacopoeia only included Jiang Huang and Yu Jin which contains curcumin, while curcumin is not included.
antiedemic, antiinflammatory, bile stimulant; antibacterial, antifungal, lipo/cyclooxygenase inhibitor
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H225-H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P305+P351+P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements | 26 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MI5230000 |
| Hazard Note | Irritant |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29145000 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 458-37-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 Oral-Rat-12.200 mg/kg |