A1046312
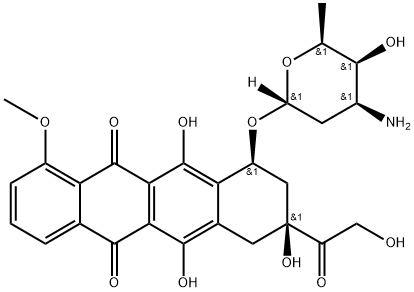
Adriamycin , 97% , 23214-92-8
CAS NO.:23214-92-8
Empirical Formula: C27H29NO11
Molecular Weight: 543.53
MDL number: MFCD00869292
EINECS: 245-495-6
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | RMB399.20 | In Stock |
|
| 100MG | RMB1007.20 | In Stock |
|
| 500MG | RMB3199.20 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
Update time: 2022-07-08
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 205°C |
| Boiling point: | 617.77°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3783 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | ≥27.2 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥24.8 mg/mL in H2O with ultrasonic |
| form | solid |
| pka | pKa 8.2 (Uncertain) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| InChIKey | AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-XFGIOHMQNA-N |
| SMILES | OC1C2C(C3=CC=CC(OC)=C3C(=O)C=2C(O)=C2[C@H](C[C@](O)(C(=O)CO)CC=12)O[C@]1([H])O[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](N)C1)=O |&1:18,20,29,32,34,36,r| |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 23214-92-8 |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 10, Sup 7) 1987 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Doxorubicin (23214-92-8) |
Description and Uses
Doxorubicin (adriamycin) is the most extensively studied of a family of highly fluorescent anthracycline antibiotics produced by several Streptomyces species, first reported in 1967 and later approved for human therapeutic use as an antitumour agent for the treatment of a wide range of cancers. Doxorubicin also exhibits anti-HIV and antibacterial activity. The mode of action of doxorubicin is thought to be due to intercalation of DNA and inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS07,GHS08 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H319-H335-H350-H362 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P263-P280 |
| HS Code | 2941900000 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 23214-92-8(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | An anthracycline cytotoxic antineoplastic that is produced by Streptomyces peucetius. The LD50 in mice is 9.4 mg/kg, i.v. It is a carcinogen that inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis by intercalating in double-stranded DNA with the amino sugar in the minor groove and the 90-OH group of the anthracycline ring hydrogen-bonded to the adjacent guanine. It also alters membrane fluidity and ion transport, and generates free radicals through a cytochrome P450-mediated reductive process. In humans, it causes alopecia, stomatitis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cardiotoxicity (manifested by tachycardia), and potentially fatal congestive heart failure. |