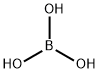
Boric acid , GR,≥99.8% , 10043-35-3
Synonym(s):
Boric acid;TBE buffer
CAS NO.:10043-35-3
Empirical Formula: BH3O3
Molecular Weight: 61.83
MDL number: MFCD00236358
EINECS: 233-139-2
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 160 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 219-220 °C (9.7513 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.440 g/cm3 |
| bulk density | 400-600kg/m3 |
| vapor pressure | 2.6 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.330-1.340 |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| pka | 8.91±0.43(Predicted) |
| form | working solution |
| color | ≤10(APHA) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.435 |
| PH | 3.6-4.4 (25℃, saturated solution in H2O) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 3.8 - 4.8 |
| Water Solubility | 49.5 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.05 |
| Merck | 14,1336 |
| BRN | 1697939 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3; STEL 6 mg/m3 |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | BUFFERING DENATURANT ANTIMICROBIAL |
| Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) | Boric acid (10043-35-3) |
| InChI | 1S/BH3O3/c2-1(3)4/h2-4H |
| InChIKey | KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | OB(O)O |
| LogP | -1.09 at 22℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10043-35-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | B(OH)3(10043-35-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Orthoboric acid (10043-35-3) |
| Absorption | ≤0.05 at 260 in H2O at 1M ≤0.05 at 280 in H2O at 1M |
Description and Uses
Boric acid is a monobasic acid that exhibits extremely weak acidity (Ka = 5.8 × 10⁻¹⁰), similar to silicic acid (K₁ = 2 × 10⁻¹⁰). Upon ionisation in water, it does not donate protons directly but instead forms a complex with hydroxide ions present in the solution:H₃BO₃ + 2H₂O → H₃O⁺ + B(OH)₄⁻
This behaviour is related to the electron-deficient nature characteristic of boron compounds. In boric acid, the boron atom acts as an electron pair acceptor by bonding with a hydroxide ion, where the oxygen atom serves as the electron pair donor. Thus, boric acid is considered a typical Lewis acid.
When glycerol or mannitol [CH₂(OH)(CHOH)₄CH₂OH] is added to a boric acid solution, its acidity increases. This is because boric acid forms a coordination complex (anion) with glycerol, which facilitates the release of H⁺ ions, thereby enhancing ionisation.
In the crystal structure of boric acid, the fundamental unit is the planar triangular BO₃ group. Each boron atom undergoes sp² hybridisation, and each oxygen atom forms a covalent bond with a boron atom, while also interacting with two hydrogen atoms through covalent and hydrogen bonding. These interactions give rise to layered, sheet-like macromolecular structures. Upon heating, the weak hydrogen bonds are disrupted, leading to disintegration of the macromolecular sheets and an increase in solubility.
Boric acid can be used to study molecular biology, DNA and RNA purification, biological buffers and molecular biology reagents. Boric acid has been used to test the toxic effects of boron on growth and antioxidant system parameters of maize (Zea mays L.) roots. Boric acid has also been used to study the effect of time period after boric acid injection on (10)B absorption in different regions of adult male rat′s brain.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS08 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H360FD |
| Precautionary statements | P201-P202-P280-P308+P313-P405-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi,T,Xn |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38-60-63-62-61 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36-53-45-37/39-36/37/39-22-24/25-23 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | ED4550000 |
| F | 3 |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HS Code | 28100090 |
| Storage Class | 6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects |
| Hazard Classifications | Repr. 1B |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 10043-35-3(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 5.14 g/kg (Smyth). |