A2493712
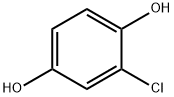
2-Chlorohydroquinone , ≥85.0%(GC) , 615-67-8
Synonym(s):
2-Chloro-1,4-dihydroxybenzene
CAS NO.:615-67-8
Empirical Formula: C6H5ClO2
Molecular Weight: 144.56
MDL number: MFCD00002341
EINECS: 210-442-8
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 1G | RMB39.20 | In Stock |
|
| 5G | RMB47.20 | In Stock |
|
| 25G | RMB158.40 | In Stock |
|
| 100G | RMB463.20 | In Stock |
|
| 500G | RMB2236.80 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
Update time: 2022-07-08
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 100-104 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 263 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.2558 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4620 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 263°C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 9.21±0.18(Predicted) |
| form | Fine Crystalline Powder |
| color | Light brown to gray |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| BRN | 636835 |
| InChI | 1S/C6H5ClO2/c7-5-3-4(8)1-2-6(5)9/h1-3,8-9H |
| InChIKey | AJPXTSMULZANCB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Oc1ccc(O)c(Cl)c1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 615-67-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,4-Benzenediol, 2-chloro-(615-67-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chlorohydroquinone (615-67-8) |
Description and Uses
Chlorohydroquinone is a component of polyethers based on organotin with potential application to breast cancer treatment via growth inhibition. Also a component in the synthesis of contraceptive agents in pharmaceutical compounds. It is also used within hydroxylation and catalysis organic reactions in the synthesis of pharmacologically active phenolic compounds.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS05,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H315-H317-H318-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P280-P280-P305+P351+P338+P310 |
| target organs | Respiratory system |
| PPE | dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi |
| Risk Statements | 21-36/37/38-43 |
| Safety Statements | 36/37-37/39-26 |
| RIDADR | UN2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MX4800000 |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HazardClass | 6.1 |
| PackingGroup | III |
| HS Code | 29081990 |
| Storage Class | 11 - Combustible Solids |
| Hazard Classifications | Eye Dam. 1 Skin Irrit. 2 Skin Sens. 1 STOT SE 3 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 615-67-8(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | An antidiarrhea drug used extensively in Japan. It has been shown to be the cause of subacute myelooptic neuropathy, a syndrome in which stiffness of the joints is accompanied by damage to the optic nerve. |