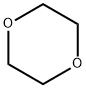
Dioxane , standardforGC,≥99.7%(GC) , 123-91-1
Synonym(s):
Dioxane;1,4-Dioxane;1.4-Dioxane;1,4-Dioxane solution;Diethylene oxide
CAS NO.:123-91-1
Empirical Formula: C4H8O2
Molecular Weight: 88.11
MDL number: MFCD00006571
EINECS: 204-661-8
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 12 °C |
| Boiling point: | 101 °C |
| Density | 1.034 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 27 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 54 °F |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | Soluble in acetone, alcohol, benzene, and ether (Weast, 1986). Miscible with most organic
solvents (Huntress and Mulliken, 1941) including 2-methylpropanol, toluene, cychexanone, and
cyclopentanone. |
| form | Solution |
| color | APHA: ≤20 |
| PH | 6-8 (500g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Mild ether-like odor detectable at 0.8 to 172 ppm (mean = 12 ppm) |
| explosive limit | 1.7-25.2%(V) |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 220 nm Amax: ≤0.70 λ: 235 nm Amax: ≤0.50 λ: 250 nm Amax: ≤0.20 λ: 270 nm Amax: ≤0.10 λ: 295-400 nm Amax: ≤0.01 |
| Merck | 14,3300 |
| BRN | 102551 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 4.89(x 10-6 atm?m3/mol) (static headspace-GC, Welke et al., 1998) |
| Dielectric constant | 2.2(25℃) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 25 ppm (≈90 mg/m3) (ACGIH),
100 ppm (MSHA and OSHA); carcinogenicity:
Animal Sufficient Evidence (IARC). |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, oxygen, halogens, reducing agents, moisture. Highly flammable - note wide explosive range. May form explosive peroxides in storage (rate of formation increased by heating, evaporation or exposure to light). |
| InChI | 1S/C4H8O2/c1-2-6-4-3-5-1/h1-4H2 |
| InChIKey | RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1COCCO1 |
| LogP | -0.42 at 20℃ |
| Surface tension | 32.71mN/m at 293.15K |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 123-91-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 11, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,4-Dioxane(123-91-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,4-Dioxane (123-91-1) |
| ECETOC JACC REPORT | 1,4-Dioxane (123-91-1) |
Description and Uses
1,4-dioxane is a clear liquid with ether-like odour. It is highly flammable and forms explosive peroxides in storage (rate of formation increased by heating, evaporation, or exposure to light). 1,4-Dioxane is incompatible with oxidising agents, oxygen, halogens, reducing agents, and moisture. Industrial applications of 1,4-dioxane are extensive, for instance, as solvent for cellulose acetate, ethyl cellulose, benzyl cellulose, resins, oils, waxes, and some dyes; as a solvent for paper, cotton, and textile processing; and for various organic and inorganic compounds and products. It is also used in automotive coolant liquid and in shampoos and other cosmetics as a degreasing agent and as a component of paint and varnish. Human exposures to 1,4-dioxane have been traced to multiple occupations and breathing of contaminated workplace air and drinking polluted water. Industrial uses of 1,4-dioxane are very many. For instance, it is used as solvent for celluloses, resins, lacquers, synthetic rubbers, adhesives, sealants, fats, oils, dyes, and protective coatings; as a stabiliser for chlorinated solvents and printing inks; and as a wetting and dispersing agent in textile processing agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals, in different processing of solvent-extraction processes, and in the preparation and manufacture of detergents.
1,4-Dioxane, the six-member cyclic diether, is used as an aluminum inhibitor in chlorinated solvents like 1,1,1-trichloroethane and as a solvent for certain resins and polymers.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS07,GHS08 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H225-H304-H315-H319-H335-H340-H350-H372-H412 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P273-P301+P310-P303+P361+P353-P305+P351+P338-P331 |
| target organs | Respiratory system |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,F,T |
| Risk Statements | 45-46-11-36/38-48/23/24/25-65-66-40-36/37-19-41-37/38-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-48/20/22-38-22-36/37/38-10 |
| Safety Statements | 9-16-36/37-46-45-53-7-62-26-24/25-23-S9-S46-S36/37-S16 |
| RIDADR | UN 1993 3/PG 2 |
| OEL | Ceiling: 1 ppm (3.6 mg/m3) [30-minute] |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | JG8225000 |
| F | 8 |
| Autoignition Temperature | 180 °C |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HazardClass | 3 |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29329990 |
| Storage Class | 3 - Flammable liquids |
| Hazard Classifications | Carc. 1B Eye Irrit. 2 Flam. Liq. 2 STOT SE 3 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 123-91-1(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 in mice, rats (ml/kg): 5.7, 5.2 orally (Laug) |
| IDLA | 500 ppm |
| Limited Quantities | 1.0 L (0.3 gallon) (liquid) |
| Excepted Quantities | Max Inner Pack (30g or 30ml) and Max Outer Pack (500g or 500ml) |