PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 168-170 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 232.96°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | +79.0~+81.0°(D/20℃) (c=10, dil. NH4OH) |
| Density | 1,5 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 80 ° (C=10, H2O) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | H2O: 100 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pK1:12.35 (25°C) |
| color | White |
| PH | 4.5-6.0 (H2O)Aqueous solution |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 5 - 7 at 180 g/l at 25 °C |
| biological source | bovine (Ruminant- CowOxBuffalo) |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +80±1°, 24 hr, c = 5% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,4335 |
| BRN | 1724619 |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | SKIN CONDITIONING |
| InChI | 1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h1,3-6,8-12H,2H2/t3-,4+,5+,6-/m0/s1 |
| InChIKey | GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-DPYQTVNSSA-N |
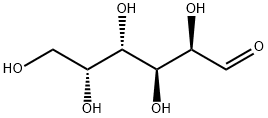
| SMILES | OC[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=O |
| LogP | -2.490 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 59-23-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | D-Galactose(59-23-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Galactose (59-23-4) |
Description and Uses
D-Galactose is a monosaccharide sugar that serves as an energy source and glycosylation component. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose and often used as a source of carbon in culture media. Galactose is a component of the disaccharide lactose and released upon hydrolysis by β-galactosidase enzymes. It is converted to glucose via the Leloir pathway or metabolized via an alternative pathway, such as the DeLey-Doudoroff pathway.
Galactose is a simple monosaccharide used as a component of the galactosyltransferase labeling buffer. It serves as an energy source and an important constituent of glycolipids and glycoproteins. Since it is a component of antigens, it plays a vital role in the determination of blood type within the ABO blood group system.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302-H312-H332 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P264-P270-P271-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P304+P340-P330-P363-P501 |
| PPE | Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US) |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements | 22-24/25-36/37/39-27-26 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | LW5490000 |
| F | 3 |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HS Code | 29400090 |
| Storage Class | 11 - Combustible Solids |