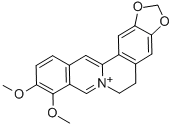
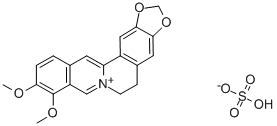
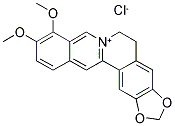
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 204-206 °C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 486.8°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2976 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.47(at 25℃) |
| color | White to yellow crystals |
| Water Solubility | 43.48g/L(25 ºC) |
| LogP | -0.990 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 2086-83-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Description and Uses
Coptis chinensis was widely used in China as a folk medicine by Shennong around 3000 BC. Coptis chinensis was first described in the ancient Chinese medical book The Divine Farmer's Herb-Root Classic. Coptis chinensis was used to treat intestinal bacterial infections and antipyretic analgesic for thousands of years ago
Coptis chinensis also called zhilian, chuanlian, weilian, jizhualian, shanglian, and xuanlian in Chinese history. Coptis chinensis was accepted by most physicians, and the Chinese pharmacopoeia also uses Coptis chinensis as its official name. Coptis chinensis mainly grows in Anhui, Hunan, Sichuan, and Yunnan and has been cultivated in Sichuan since the Ming dynasty, which has a long history of cultivation. Other species of Coptis chinensis from different places were used as medicine. However, commodity circulation of wild Rhizoma coptidis has not been formed . Coptis chinensis is national three level protection plants at present and majorly produced in Shizhu of Chongqing, West Hubei, Shanxi, and Gansu.
Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of isoquinoline alkaloids. It is found in some plants such as huanglian (Rhizoma coptidis), huangbo (Phellodendri Chinensis) Cortex), sankezhenthree needles (Berberidis Radix), and so on.
The components of Coptis chinensis which have antibacterial and antiinflammatory effects are original alkaloid berberine class, including berberine, coptisine, palmatine, epiberberine, columbamine, jatrorrhizine, worenine, and magnoflorine, with berberine having the highest content (5–8%).
Antiseptic drug.Treat intestinal infection caused from dysentery bacillus and E.coil
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 |
| RIDADR | 1544 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | DR9866400 |
| F | 3-10 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) |
| PackingGroup | III |
| Toxicity | LD50 orl-mus: 329 mg/kg YKKZAJ 82,726,62 |