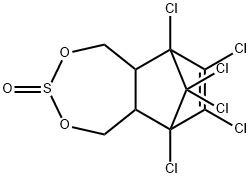
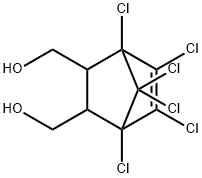
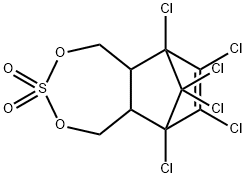
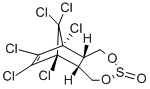
α-EndosulfanD4 , 100ng/μL solution: acetone , 115-29-7
CAS NO.:115-29-7
Empirical Formula: C9H6Cl6O3S
Molecular Weight: 406.93
MDL number: MFCD00137651
EINECS: 204-079-4
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 106°C |
| Boiling point: | 106 °C(Press: 0.70 Torr) |
| Density | 1.7450 |
| vapor pressure | 8.3 x 10-4 Pa (25 °C) for 2:l mixture of
α- and β-isomers |
| Flash point: | -26 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Sparingly) |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 23 ºC |
| Merck | 13,3608 |
| BRN | 2062338 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 115-29-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Endosulfan(115-29-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Endosulfan (115-29-7) |
Description and Uses
Endosulfan (70) [115-29-7], 6,7,8,9,10,10- hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-2,4,3,- benzo-dioxathiepine 3-oxide (IUPAC) [The technical product is a mixture of two isomers: α-endosulfan: 3α,5αβ,6α, 9α,9αβ (64–67%) (70a) and β-endosulfan 3α,5aα,6β,9β, 9aα, (29–32%) (70b)]; [959-98-8] (formerly [33213-66- 0]) (β-endosulfan);[33213-65-9] (formerly [891-86-1] and [19670-15-6]) (β-endosulfan) is the adduct of hexachlorocyclopentadiene and 1,4-dihydroxy-2-butene reacted further with SOCl2 to produce 6,7,8,9,10,10-hexachloro- 1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-2,4,3-benzodioxa thiepin-3-oxide. The technical product is a brownish solid, mp 70–100 ?C, vapor pressure 1.3 mPa at 25 ?C, soluble in petroleum solvents but having low solubility in water. It consists of about four parts of α-isomer (mp 108 ?C, cis with regard to the sulfite group) and one part of the β-isomer (mp 206 ?C, trans with regard to the sulfite group). The α-isomer, which is somewhat more insecticidal, is slowly converted to the more stable β-isomer at high temperature, and both isomers are oxidized slowly to endosulfan sulfate [1031-07-8] (mp 181 ?C). In acid media, both isomers form endosulfan diol [2157-19-9] (mp 203 ?C).
Endosulfan is used for the control of sucking, chewing, boring insects and mites on a wide variety of crops. It also controls tsetse flies.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS09 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H300+H310+H330-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P262-P273-P280-P302+P352+P310-P304+P340+P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T,N,Xn,F,T+ |
| Risk Statements | 24/25-36-50/53-67-65-62-51/53-48/20-38-11-26/28-21 |
| Safety Statements | 28-36/37-45-60-61-62-63-33-29-16-9 |
| RIDADR | UN 2761 |
| OEB | D |
| OEL | TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 [skin] |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RB9275000 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29209090 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 115-29-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in male, female rats: 43, 18 mg/kg (Gaines) |