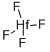Hafnium , 99.9%metalsbasis,1-10mm , 7440-58-6
Synonym(s):
Celtium;Hafnium;Hafnium element
CAS NO.:7440-58-6
Empirical Formula: Hf
Molecular Weight: 178.49
MDL number: MFCD00011032
EINECS: 231-166-4
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 2227 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 4602 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 13.3 g/cm3 (lit.) |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | soluble in HF |
| form | wire |
| Specific Gravity | 13.31 |
| color | Silver-gray |
| Flame Color | White |
| Resistivity | 29.6 μΩ-cm, 0°C |
| Water Solubility | soluble HF; slowly reacts with conc H2SO4, aqua regia [KIR80] |
| Merck | 13,4603 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: Ceiling 2 ppm OSHA: Ceiling 5 ppm(7 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 50 ppm; Ceiling 5 ppm(7 mg/m3) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxygen, sulfur, strong oxidizing agents, halogens, phosphorus, strong acids. Highly flammable. |
| InChIKey | VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-58-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hafnium (7440-58-6) |
Description and Uses
De scription: Hafnium is a refractory metal which occurs innature in zirconium minerals. Molecular weight= 178.49;Specific gravity (H2O:1)= 13.31; Boiling point = 4602℃; .Freezing/Melting point = 2227℃; Vapor pressure= 1 X .10~4 mmHg at 20℃. Insoluble in water.
Hafnium has a great affinity for absorbing slow neutrons. This attribute, along with itsstrength and resistance to corrosion, makes it superior to cadmium, which is also used formaking control rods for nuclear reactors. This use is of particular importance for the type ofnuclear reactors used aboard submarines. By moving the control rods in and out of a nuclearreactor, the fission chain reaction can be controlled as the neutrons are absorbed in the metalof the rods. The drawback to hafnium control rods is their expense: it costs approximately onemillion dollars for several dozen rods for use in a single nuclear reactor.
In vacuum tubes and other applications that must have gases removed, hafnium is used asa “getter” to absorb any trace oxygen or nitrogen in the tube, thus extending the life of thevacuum tube. Hafnium’s qualities also make it ideal for filaments in light bulbs and, whenmixed with rare-earth metals, as a “sparking” misch metal. Hafnium is also used to a lesserextent as an alloying agent for several other metals, including iron, titanium, and niobium.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS02 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H228 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P240-P241-P280-P370+P378 |
| Hazard Codes | F,Xn,T |
| Risk Statements | 11-20/21/22-34-23/24/25 |
| Safety Statements | 9-16-26-27-33-36-36/37/39-45-28 |
| RIDADR | UN 3178 4.1/PG 3 |
| OEB | C |
| OEL | TWA: 0.5 mg/m3 [*Note: The REL also applies to other hafnium compounds (as Hf).] |
| WGK Germany | - |
| RTECS | MG4600000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 3822 00 00 |
| HazardClass | 8 |
| PackingGroup | III |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 7440-58-6(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| IDLA | 50 mg Hf/m3 |