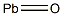Lead oxide yellow , 99.999%metalsbasis, orthogonal crystal system , 1317-36-8
Synonym(s):
Lead monoxide;Lead(II) oxide
CAS NO.:1317-36-8
Empirical Formula: OPb
Molecular Weight: 223.199
MDL number: MFCD00011164
EINECS: 215-267-0
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 886 °C(lit.) |
||||||||||||||
| Boiling point: | 1470 °C |
||||||||||||||
| Density | 9.53 |
||||||||||||||
| bulk density | 3500-3700kg/m3 |
||||||||||||||
| vapor pressure | 10 mm Hg ( 0 °C) |
||||||||||||||
| refractive index | 2.67 |
||||||||||||||
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
||||||||||||||
| solubility | Soluble in concentrated alkali, HCl and ammonium chloride. Insoluble in dilute alkali and alcohol. |
||||||||||||||
| form | powder |
||||||||||||||
| color | yellow |
||||||||||||||
| Specific Gravity | 9.53 |
||||||||||||||
| PH | 8-9 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
||||||||||||||
| Water Solubility | Soluble in concentrated alkali, hydrochloric acid, and ammonium chloride. Insoluble in water, dilute alkali and alcohol. |
||||||||||||||
| Crystal Structure | Rutile type |
||||||||||||||
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 4: no reaction with water under neutral conditions |
||||||||||||||
| Merck | 14,5413 |
||||||||||||||
| crystal system | square |
||||||||||||||
| Space group | P42/mnm |
||||||||||||||
| Lattice constant |
|
||||||||||||||
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.05 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 0.050 mg/m3 |
||||||||||||||
| Stability: | Stable. Reacts violently with hydrogen peroxide, strong oxidizing agents, aluminium, zirconium, halogens, sulphur trioxide, boron, silicon, sodium, zinc. |
||||||||||||||
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1317-36-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
||||||||||||||
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Lead monoxide(1317-36-8) |
||||||||||||||
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead monoxide (1317-36-8) |
Description and Uses
Lead(II) oxide occurs in two polymorphs, red, having a tetragonal crystal structure and yellow, having an orthorhombic crystal structure. Both forms occur naturally as rare minerals. The red form is known as “Litharge” and the yellow form is known as “Massico”.
Lead(II) oxide is employed mostly in lead-based industrial glass and industrial ceramics, including computer components. It is used as an intermediate/precursor in the manufacture of several products, for example water proof cements, lubricants, lubricating oils, inorganic pigments, lead soaps, petroleum refining, rubber, cathode ray tube glass, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). It is useful for lead acid batteries as cathode and anode. Lead monoxide scores significant applications in oil, gas and chemical manufactures. It is an efficient catalyst for condensation reactions in organic synthesis.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H302+H332-H351-H360D-H362-H372-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P263-P273-P301+P312-P304+P340+P312-P308+P313 |
| Hazard Codes | T,N |
| Risk Statements | 61-20/22-33-50/53-62 |
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 2291 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | OG1750000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 2824 10 00 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) |
| PackingGroup | III |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 1317-36-8(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in rats: 40 mg Pb/100g (Bradley, Fredrick) |