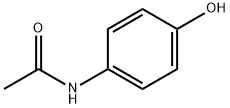
4-Acetamidophenol , Analysis of standard products, ≥99.5% , 103-90-2
Synonym(s):
Paracetamol;Acetaminophen;APAP;4-Acetamidophenol;N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)acetamide
CAS NO.:103-90-2
Empirical Formula: C8H9NO2
Molecular Weight: 151.16
MDL number: MFCD00002328
EINECS: 203-157-5
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 250MG | RMB94.40 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 168-172 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 273.17°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1,293 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 0.008Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5810 (rough estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble0.5M, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 9.86±0.13(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| PH | 5.5-6.5 (H2O, 20℃)(saturated solution) |
| PH Range | 5.5 - 6.5 (H?O, 20 °C) (saturated solution) |
| Odor | odorless |
| explosive limit | 15%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 14 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,47 |
| BRN | 2208089 |
| BCS Class | 3,4 |
| Major Application | pharmaceutical (small molecule) |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | SKIN CONDITIONING |
| InChI | 1S/C8H9NO2/c1-6(10)9-7-2-4-8(11)5-3-7/h2-5,11H,1H3,(H,9,10) |
| InChIKey | RZVAJINKPMORJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)Nc1ccc(O)cc1 |
| LogP | 1.098 at 25℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 103-90-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetaminophen(103-90-2) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 50, 73) 1999 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetaminophen (103-90-2) |
Description and Uses
Acetaminophen is an analgesic and antipyretic compound. Unlike many NSAIDs, which inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, early studies suggested that acetaminophen is a poor inhibitor of both isoforms. However, it does inhibit COX-2 by 83% and COX-1 by 56% in human blood ex vivo, albeit at a high 1,000 mg dose, with IC50 values of 25.8 and 113.7 μM, respectively. Acetaminophen is enzymatically and non-enzymatically converted to several reactive metabolites that contribute to adverse or indirect effects, including liver injury. At toxic doses, the acetaminophen metabolite N-acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI; ) depletes glutathione reserves in the liver, leading to an accumulation of NAPQI and subsequent hepatocyte necrosis. Acetaminophen decreases glutathione levels and reduces glutathione peroxidase activity in mice when administered at a dose of 250 mg/kg and induces ferroptotic cell death in primary mouse hepatocytes, an effect that can be blocked by the ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1 . Acetaminophen has analgesic and antipyretic properties in animal models.
manufacture of azo dyes, photographic chemicals.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P270-P301+P312-P501 |
| PPE | dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,T,F |
| Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38-52/53-36/38-40-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36-61-37/39-22-45-36/37-16-7 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG III |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | AE4200000 |
| Autoignition Temperature | 540 °C |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HazardClass | 9 |
| PackingGroup | III |
| HS Code | 29242930 |
| Storage Class | 11 - Combustible Solids |
| Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 4 Oral |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 103-90-2(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 in mice (mg/kg): 338 orally (Starmer), 500 i.p. (Dahlin, Nelson) |