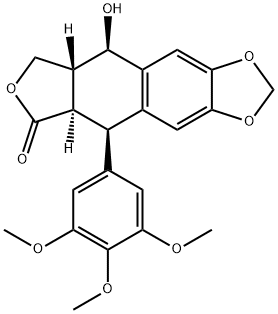
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 183-184 °C (lit.) |
| alpha | -110.7 º (c=1, CHCl3) |
| Boiling point: | 453.31°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2649 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4480 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO:15.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);36.2(Max Conc. mM) |
| pka | 13.26±0.40(Predicted) |
| form | Powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| optical activity | [α]/D 131±2°, c = 1 in chloroform |
| Merck | 13,7628 |
| BRN | 99163 |
| Stability: | Very Hygroscopic |
| InChIKey | YJGVMLPVUAXIQN-XVVDYKMHSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cc(cc(OC)c1OC)[C@H]2C3C(COC3=O)[C@@H](O)c4cc5OCOc5cc24 |
| LogP | 2.010 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 518-28-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Description and Uses
Podophyllotoxin (2,3-butyl-4-aromatic naphthene) is isolated from guijiu(Podophyllum) . There are two species as the main source of podophyllotoxin,
Podophyllum hexandrum Royle and Podophyllum peltatum .
Although podophyllotoxin has significant antitumor and antiviral activities, it
showed several toxicity and side effects. Podophyllotoxin derivatives, etoposide
(VP-16-213), Etopophos, amino sugar etoposide (NK6l1), and teniposide (VM26),
have been developed as anticancer drugs. They are used to treat small cell lung cancer, testicular cancer, acute leukemia, malignant lymphoma, etc. But podophyllotoxin derivatives are not free of toxicity. Besides the narrowing of the anticancer
spectrum and low water solubility, these drugs could induce severe myelosuppression, gastrointestinal side effects, etc.
Although the synthetic and biosynthetic pathways of podophyllotoxin have been
elucidated, it is still the most effective, economic, and fast way to extract podophyllotoxin from the plant.
antineoplastic, inhibits microtubule assembly, and human DNA topoisomerase II; antimitotic agent
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS06 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301+H311+H331-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P280-P301+P310-P302+P352+P312-P304+P340+P311-P305+P351+P338 |
| target organs | Respiratory system |
| PPE | Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Statements | 21-25-36/37/38-23/25-23/24/25 |
| Safety Statements | 36/37/39-45-26 |
| RIDADR | UN 3462 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | LV2500000 |
| F | 1-8-10 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29189090 |
| Storage Class | 6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 very toxic hazardous materials |
| Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 3 Dermal Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation Acute Tox. 3 Oral Eye Irrit. 2 Skin Irrit. 2 STOT SE 3 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 518-28-5(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 in rats (mg/kg): 8.7 i.v.; 15 i.p. (Phillips) |
| Limited Quantities | 100ml (liquid) or 0.5 Kg (solid) |
| Excepted Quantities | Max Inner Pack (1g or 1ml) and Max Outer Pack (500g or 500ml) |