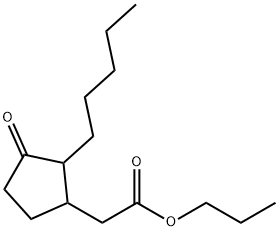
Prohydrojasmonracemate , 10mMinDMSO , 158474-72-7
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 1ml | RMB159.20 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
PRODUCT Properties
| Boiling point: | 340.2±15.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 0.967±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Hexane (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Oil |
| color | Pale Yellow to Light Yellow |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C15H26O3/c1-3-5-6-7-13-12(8-9-14(13)16)11-15(17)18-10-4-2/h12-13H,3-11H2,1-2H3 |
| InChIKey | IPDFPNNPBMREIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(CC(OCCC)=O)CCC(=O)C1CCCCC |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cyclopentaneacetic acid, 3-oxo-2-pentyl-, propyl ester (158474-72-7) |
Description and Uses
Prohydrojasmon (PDJ) [propyl(1RS,2RS)-(3-oxo-2-pentylcyclopentyl) acetate], an analog of Jasmonic acid (JA), was first registered as a plant growth regulator, particularly for coloring apples and grapes. Plant growth regulators are naturally or chemically synthesized substances that play roles in plants' developmental or metabolic processes. Subsequently, similar to JA, PDJ was found to induce direct and indirect defenses against herbivores in non-infested plants[1].
Prohydrojasmon (PDJ), as a plant growth regulator, focuses on fruits, including apples, oranges, mangoes, and grapes. Specifically, it has been applied to enhance mango and red pear fruit coloration. PDJ treatment of crops increases their direct and indirect defenses against several insect pests under open field conditions. A report on PDJ treatment of non-infested maize plants suggests a reduction in the weights and survival rates of the common armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker), larvae and their increased attraction to Cotesia kariyai Watanabe, a parasitoid wasp of the herbivore. Furthermore, two-spotted spider mites (Tetranychus urticae Koch) laid significantly fewer eggs on PDJ-treated leaf disks than on control leaf disks. PDJ treatment of non-infested lima bean plants induced the production of volatiles, including (E)-β-ocimene and (E)-4,8-dimethyl-1,3,7-nonatriene (DMNT), which attract Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot, a predatory mite. Moreover, under greenhouse conditions, PDJ treatment of tomato plants negatively affects the damage caused by thrips[3].
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H412-H319-H335-H315 |
| Precautionary statements | P273-P501-P264-P280-P302+P352-P321-P332+P313-P362-P264-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313P |