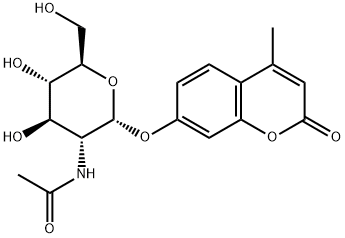
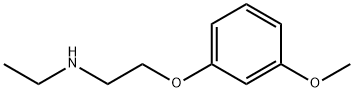
4-Methylumbelliferyl 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-a-D-galactopyranoside , ≥95% , 124223-99-0
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 5mg | RMB2134.40 | In Stock |
|
| 10mg | RMB3131.20 | In Stock |
|
| 25mg | RMB5983.20 | In Stock |
|
| 50mg | RMB8676.80 | In Stock |
|
| 100mg | RMB14064.00 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 257-260°C |
| Boiling point: | 732.2±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.47±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.87±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 124223-99-0 |
Description and Uses
4-Methylumbelliferyl 2-acetoamido-2-deoxy-α-D-galactopyranoside (4-MU-2-acetoamido-2-deoxy-α-Gal) is a fluorogenic substrate used to quantify α- and β-galactopyranosaminidase activity. 4-MU-2-acetoamido-2-deoxy-α-Gal is cleaved by α- and β-galactopyranosaminidase to release the fluorescent moiety 4-MU. 4-MU fluorescence is pH-dependent with excitation maxima of 320 and 360 nm at low (1.97-6.72) and high (7.12-10.3) pH, respectively, and an emission maximum ranging from 445 to 455 nM, increasing as pH decreases.
An effective substrate for the detection of N-acetyl-a-D-Galactopyranosiaminidase activity. The deficiency of this enzyme is the defect in Schindler disease