PRODUCT Properties
| Density | 1.54±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| form | stable only in solution |
| pka | pK (25°) 3.35 |
| color | stable only in solution |
| PH | 3.28(1 mM solution);2.67(10 mM solution);2.13(100 mM solution) |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | SOLVENT HUMECTANT |
| InChI | InChI=1S/HNO2/c2-1-3/h(H,2,3) |
| InChIKey | IOVCWXUNBOPUCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
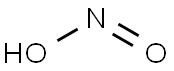
| SMILES | N(=O)O |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nitrous acid (7782-77-6) |
Description and Uses
Nitrous acid (molecular formula?HNO2) is a weak
and monobasic acid known only in solution and in the
form of nitrite salts. Nitrous acid rapidly decomposes
into nitrogen oxide, nitric oxide and water when in
solution:
2HNO2 ? NO2 + NO+H2O
It can also decompose into nitric acid and nitrous
oxide and water.
4HNO2 ? 2HNO3 +N2O +H2O
Nitric acid (HNO3), also known as “aqua fortis”
and “spirit of nitre”, is a highly corrosive and toxic
strong acid that can cause severe burns. It is colorless
when pure and a slight yellow when “glacial”. Older
samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation
of various oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as
“fuming nitric acid”.
Formation of diazotizing compounds by reaction with primary aromatic amines, source of nitric oxide.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS05 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H314 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P264-P280-P301+P330+P331-P303+P361+P353-P363-P304+P340-P310-P321-P305+P351+P338-P405-P501 |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 7782-77-6(Hazardous Substances Data) |