PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 78-82 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 280 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.899 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 6.68 at 25 °C (gas saturation-HPLC/UV spectrophotometry, Sonnefeld et al., 1983) |
| refractive index | 1.6360 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 122°C |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol, ether, and benzene (U.S. EPA, 1985) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 0.899 |
| Water Solubility | 3.93mg/L(25 ºC) |
| BRN | 774092 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.14 at 25 °C (gas stripping-UV spectrophotometry, Warner et al., 1987) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. |
| Major Application | environmental |
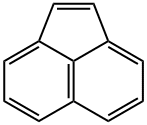
| InChI | 1S/C12H8/c1-3-9-4-2-6-11-8-7-10(5-1)12(9)11/h1-8H |
| InChIKey | HXGDTGSAIMULJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | c1cc2C=Cc3cccc(c1)c23 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 208-96-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acenaphthylene (208-96-8) |
Description and Uses
Acenaphthylene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) consisting of three fused aromatic rings. It is used in the production of plastics and serves as an intermediate in the manufacture of dyes, soaps, pigments, pharmaceuticals, insecticides, fungicides, herbicides, and plant growth regulators. It is also a precursor to naphthalic acids, naphthalic anhydride (which is used in pigment production), and can be utilized in the synthesis of resins.
The largest emissions of PAHs originate from the incomplete combustion of organic matter during industrial processes and other human activities. Major sources include:
(a) the processing of coal, crude oil, and natural gas;
(b) coking, coal conversion, petroleum refining, and the production of carbon black, creosote, coal tar, and bitumen;
(c) aluminum, iron, and steel production in plants and foundries;
(d) heating in power plants and households, as well as cooking;
(e) combustion of waste;
(f) motor vehicle emissions;
(g) environmental tobacco smoke.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as carcinogenic
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P264-P270-P301+P312-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 |
| target organs | Respiratory system |
| PPE | dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N,F,T,Xi |
| Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38-67-65-50/53-38-11-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-20 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-62-61-60-45-36/37-16-7-37/39-33-25-9 |
| RIDADR | UN 1145 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AB1254000 |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HazardClass | 9 |
| HS Code | 29029090 |
| Storage Class | 11 - Combustible Solids |
| Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 4 Oral Eye Irrit. 2 Skin Irrit. 2 STOT SE 3 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 208-96-8(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LC50 (21-d) for Folsomia fimetaria 145 mg/kg (Sverdrup et al., 2002). |
| Limited Quantities | 5.0 L (1.3 gallons) (liquid) or 5.0 kg (11 lbs) (solid) |
| Excepted Quantities | Max Inner Pack (30g or 30ml) and Max Outer Pack (1Kg or 1L) |