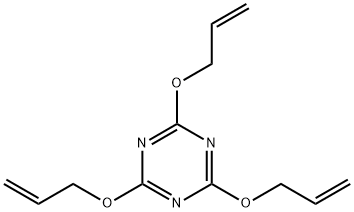
Triallyl Cyanurate , >98.0%(GC) , 101-37-1
Synonym(s):
2,4,6-Tris(allyloxy)-1,3,5-triazine;Cyanuric acid triallyl ester, Triallyl cyanurate;Triallyl cyanurate
CAS NO.:101-37-1
Empirical Formula: C12H15N3O3
Molecular Weight: 249.27
MDL number: MFCD00006049
EINECS: 202-936-7
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | 26-28 °C |
| Boiling point: | 156 °C |
| Density | 1.11 g/mL at 30 °C |
| vapor pressure | 1.3 hPa (100 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5290 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at <= 20°C. |
| solubility | 0.3g/l |
| form | Oil |
| pka | 2.04±0.10(Predicted) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.11 |
| color | Colourless |
| Water Solubility | 6g/L(20 ºC) |
| BRN | 235560 |
| Stability: | Stable, but moisture-sensitive. Incompatible with acids, peroxides, strong oxidizing agents, copper, iron and its salts. |
| InChI | 1S/C12H15N3O3/c1-4-7-16-10-13-11(17-8-5-2)15-12(14-10)18-9-6-3/h4-6H,1-3,7-9H2 |
| InChIKey | BJELTSYBAHKXRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C=CCOc1nc(OCC=C)nc(OCC=C)n1 |
| LogP | 3.51 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 101-37-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2,4,6-Triallyloxy-1,3,5-triazine(101-37-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3,5-Triazine, 2,4,6-tris(2-propenyloxy)- (101-37-1) |
Description and Uses
Polymers as monomer and modifier, organic intermediate. Triallyl Cyanurate is used preferentially as a cross-linking agent in copolymers. On heating it may polymerize violently and then isomerize to the more stable triallyl isocyanurate [1025-15-6] with the allyl groups attached to the nitrogen atoms.
At 30 ℃ viscous solutions of prepolymers form slowly. Triallyl cyanurate is used for the production of heat- and solvent-resistant coatings and moldings, reinforced plastics, and adhesives. Addition of 5 – 10% triallyl cyanurate to polyester – styrene or methyl methacrylate yields cast sheets of improved mechanical and thermal stability. Short-term heating of triallyl cyanurate with polymers in the presence of peroxides at 180 ℃ gives cross-linking; valuable copolymers are thus obtained from poly(vinyl chloride) elastomers and fluoroelastomers. Ethylene polymers and copolymers also may be crosslinked under similar reaction conditions. High-impact plastics have been obtained by grafting butyl acrylate-triallyl cyanurate copolymer with a styrene – acrylonitrile mixture. Other examples of peroxide-initiated curing with triallyl cyanurate (2 – 5 %) at 150 – 160 ℃ are polyurethanes, nylons, cellulose, polyoxyethylene, vinyl-substituted polysiloxanes, and acrylate copolymers. Crosslinking of polycarbonate with triallyl cyanurate by UV irradiation in the presence of polythiols gives scratch-resistant coatings.
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS07,GHS09 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302-H411 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P270-P273-P301+P312-P391-P501 |
| PPE | Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N |
| Risk Statements | 22-51/53 |
| Safety Statements | 36-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | XZ2080000 |
| F | 21 |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HS Code | 2933 69 80 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) |
| PackingGroup | III |
| Storage Class | 11 - Combustible Solids |
| Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 4 Oral Aquatic Chronic 2 |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 753 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit > 2000 mg/kg |