Guar , Viscosity: 5000-5500CPS, 200 measuring items , 9000-30-0
Synonym(s):
Gum guar
CAS NO.:9000-30-0
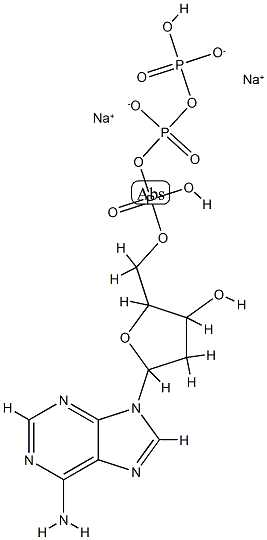
Empirical Formula: C10H14N5Na2O12P3
Molecular Weight: 535.145
MDL number: MFCD00131250
EINECS: 232-536-8
| Pack Size | Price | Stock | Quantity |
| 500G | RMB50.40 | In Stock |
|
| 2.5KG | RMB196.00 | In Stock |
|
| 5KG | RMB399.20 | In Stock |
|
| others | Enquire |
PRODUCT Properties
| Melting point: | >220°C (dec.) |
| alpha | D25 +53° (1N NaOH) |
| Density | 0.8-1.0 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.34 |
| FEMA | 2537 | GUAR GUM (CYAMOPSIS TETRAGONOLOBUS (L.)) |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | It yields a mucilage of variable viscosity when dissolved in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | Free Flowing Powder |
| color | Yellow-white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 5.0-7.0 (25°C1% in water) |
| Merck | 13,4588 / 13,4587 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. A mixture of air and finely-divided powder is potentially explosive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Cosmetics Ingredients Functions | FILM FORMING BINDING FRAGRANCE SKIN CONDITIONING VISCOSITY CONTROLLING EMULSION STABILISING ANTIOXIDANT |
| Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) | Guar gum (9000-30-0) |
| InChIKey | JEKDCIBJADJZSK-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| SMILES | P(=O)(O[H])(OP(=O)([O-])OP(=O)([O-])O[H])OC([H])([H])C1([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])(N2C([H])=NC3=C(N([H])[H])N=C([H])N=C23)O1)O[H].[Na+].[Na+] |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Guar gum (9000-30-0) |
Description and Uses
Background. Guar gum, like locust bean gum, is a galactomannan
derived from the seed of a leguminous plant. The source of guar,
Cyamopsis tetragonolobus, is widely grown in Pakistan and India
as cattle feed, and was introduced to the United States as a cover
crop in 1903. The U.S. is now also a producer. It was not until
1953, however, that guar gum was produced on a commercial
scale, primarily as a replacement for locus bean gum in the paper,
textile and food industries. The most important property of guar
is the ability to hydrate rapidly in cold water to attain a very high
viscosity. In addition to the food industry, guar is used in the
mining, paper, textile, ceramic, paint, cosmetic, pharmaceutical,
explosive, and other industries.
Sources, Harvesting, and Producing Areas. The guar is a hardy
and drought-resistant plant which grows three to six feet high with
vertical stalks. The guar pods, which grow in clusters along the
vertical stems, are about six inches long and contain 6 to 9 seeds,
which are considerably smaller than locus bean seeds. As in the
case of locust bean gum, the endosperm, which comprises 35-42%.
low calorie, soluble dietery fiber
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313P |
| PPE | Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US) |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | MG0185000 |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HS Code | 1302.39.0090 |
| Storage Class | 11 - Combustible Solids |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 9000-30-0(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 in male, female rats (g/kg): 7.35, 6.77 orally (Graham) |